Redux 是一个可预测的状态容器,用于 JavaScript 应用。它解决了 React 应用中数据共享和组件通信的问题,提供了一套标准且严格的状态管理方案。本文介绍 Redux 的核心概念、工作原理和使用方法。
一、什么是 Redux
这里借用官方的一句描述: A Predictable State Container for JS Apps 。其本质就是一个状态管理的扩展包,由 Facebook 于 2015 年提出并开源,类似 Vue 生态下的 vuex。它本身和 React 没有直接关系,只是在 React 生态的长期发展过程中,Redux 赢得了开发者的喜爱,并且和 React 师出同门,可能是最受欢迎的状态管理包。
二、解决什么问题
React 的推出大大提高了前端程序员的开发效率。其组件化的设计思想,高效的 JSX 语法,以及活跃的技术社区,迅速让 React 成为当年的前端热门框架。但是由于其本身只是采用虚拟 DOM 的方式来构建前端界面,所以对于企业级应用中组件之间如何交互,并没有提供一套完整的解决方案,其中最核心的两个问题是:
- 数据如何共享:比如全局应用状态,用户登陆信息等
- 模块如何通信:父子级组件,完全独立的多个组件之间
为了解决上述问题,Facebook 官方推出了 Redux,提供了一套标准且严格的状态管理方案,为企业级的应用开发注入了新的 Buff。
三、技术架构
在谈论 Redux 的技术架构前,我们需要先了解一些周边知识,方便我们对 Redux 的核心思想有更深一步的理解。
设计思想
- 响应式编程:Rx-Programming
- 面向数据流和变化传播的编程范式,旨在简化事件驱动应用的实现。响应式编程专注于如何创建依赖于变更的数据流并对变化做出响应。简单理解为:你给我一个变化,我做出一个反馈。
- 场景模拟:自然界就属于一个响应式编程方式的场景。
- 发布订阅模式:Pub-Sub(event-sourcing& CQRS)
- 通过将一个对象在全生命周期期间所参与的事件进行存储,方便回溯和审计。
- 命令查询职责分离
- 观察者模式:Observer-Pattern
- 当一个对象方式变化时,所有依赖它的对象都会发生变化。
设计架构
Redux 是基于单向数据流(one-way data flow)的,如下图所示:用户操作 View 层,会触发一个 Action,随后这个 Action 会更新 State(返回新的 State,而不是直接修改原先的 State),新的 State 会直接作用到 View 层,从而展示出来。
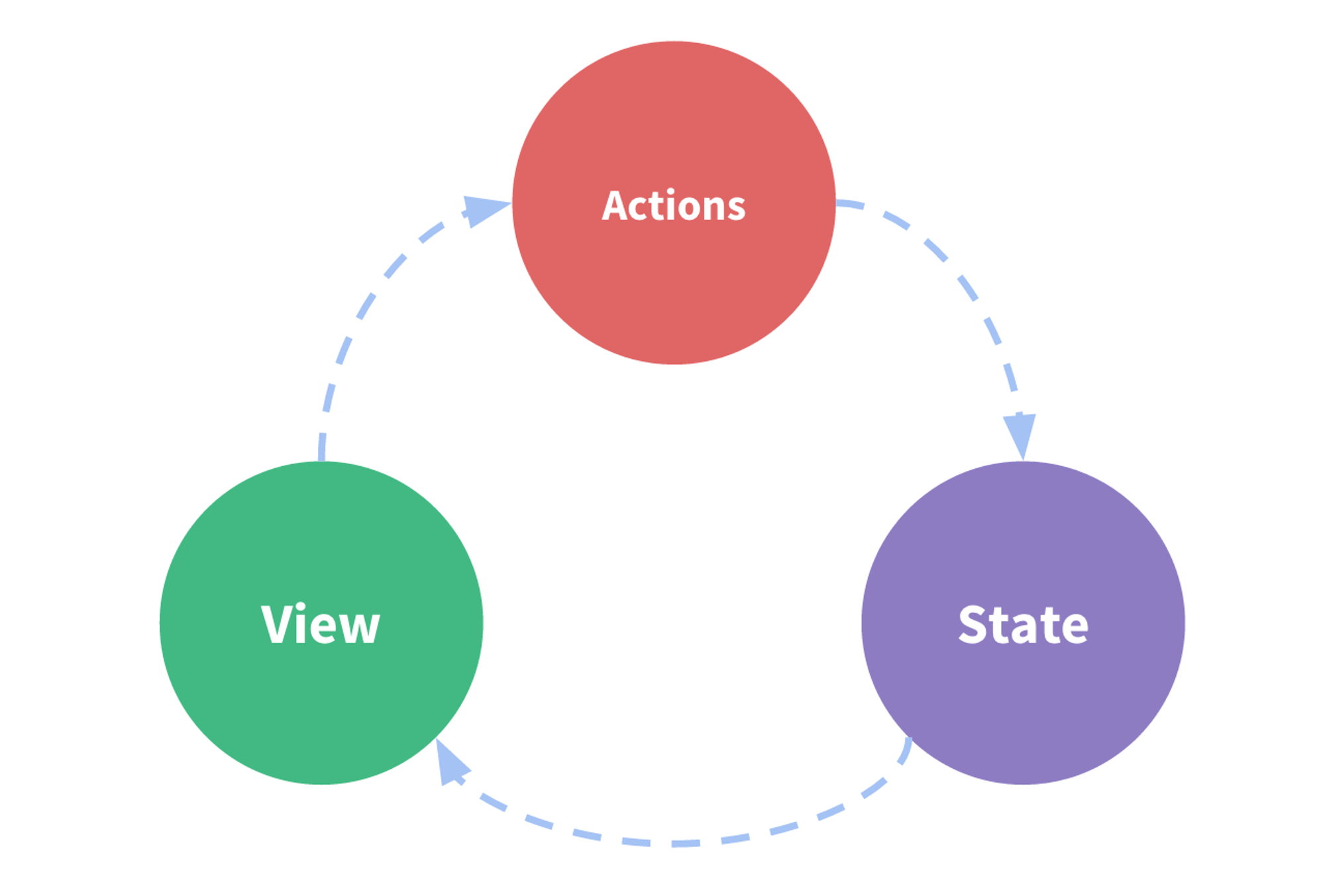
为了实现上图的效果,结合 Redux,这里罗列了如下几个重要概念:
- Store
- 全局唯一,是整个应用存放全部 State 的唯一地方;
- 将 Action 和 Reducer 进行关联
- 通过 subscribe 来订阅 State 发生变化时的回调
- 通过 unSubscribe 来取消订阅回调
- Action
- 只描述要干什么事情,不描述如何干这件事情(更新 State )
- 本质是一个包含 type 属性的 JS 对象
- 通过 store.dispatch 来进行发送
- 通过 ActionCreator 可以将多个 Action 合并到一起
- State
- 数据 State,界面 State,应用 State
- 具有不变性,不能被修改,只能被更新
- Reducer
- 纯函数,用于响应发送过来的 Action
- 接收两个参数,第一个是初始化时的 State,第二个是接收到的 Action
- 必须要有返回值(新的 State)
- Selector
四、如何使用
通过展示一个示例,我们将一个函数组件的功能改为使用 Redux 来实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
import { useState } from "react";
function Counter() {
const [counter, setCounter] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
Value: {counter}
<button onClick={() => setCounter(counter + 10)}>Withdrow</button>
<button onClick={() => setCounter(counter - 10)}>Deposit</button>
</div>
);
}
export default Counter;
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
import Counter from "./features/counter/Counter";
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<Counter />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
|
安装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
npx create-react-app my-app --template redux
npx create-react-app my-app --template redux-typescript
npm install react-redux
yarn add react-redux
install devtools for dev
npm install --save-dev redux-devtools
|
自定义 Reducer 包装类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
const createReducer =
(originalState, handlers) =>
(state = originalState, action) => {
if (Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(handlers, action.intent)) {
return handlers[action.intent](state, action);
}
return state;
};
export default createReducer;
|
自定义全局 Store 包装类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
|
class Store {
constructor(reducer) {
this.reducer = reducer;
this.subscribers = [];
this.state = this.reducer(undefined, {});
}
unsubscribeAll = () => {
this.subscribers = [];
};
subscribe = (subscriber) => {
this.subscribers.push(subscriber);
subscriber(this.state);
const unsubscribe = () => {
this.subscribers = this.subscribers.filter((item) => item !== subscriber);
};
return unsubscribe;
};
dispatch = (action) => {
this.state = this.reducer(this.state, action);
this.subscribers.forEach((subscriber) => {
subscriber(this.state);
});
};
getState = () => this.state;
}
export default Store;
|
定义模块 Reducer
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
export const COUNTER_INCREMENT = Symbol("counter Deposit");
export const COUNTER_DECREMENT = Symbol("counter Withdrow");
import { COUNTER_DECREMENT, COUNTER_INCREMENT } from "./CounterIntents";
import createReducer from "../../store/createReducer";
const getDefaultState = () => ({
value: 100,
});
const increment = (state, { payload }) => ({
...state,
value: state.value + payload,
});
const decrement = (state, { payload }) => ({
...state,
value: state.value - payload,
});
const handlers = {
[COUNTER_INCREMENT]: increment,
[COUNTER_DECREMENT]: decrement,
};
const CounterReducer = createReducer(getDefaultState(), handlers);
export default CounterReducer;
|
定义模块 Dispatcher
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
import { COUNTER_DECREMENT, COUNTER_INCREMENT } from "./CounterIntents";
const createCounterDispatcher = (store) => ({
increment: (payload) => {
const intent = COUNTER_INCREMENT;
store.dispatch({ intent, payload });
},
decrement: (payload) => {
const intent = COUNTER_DECREMENT;
store.dispatch({ intent, payload });
},
});
export default createCounterDispatcher;
|
UI 界面构建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
|
const Counter = (props) => {
const { value, increment, decrement } = { ...props };
return (
<div>
Value: {value}
<button onClick={increment.bind(this, 10)}>Deposit</button>
<button onClick={decrement.bind(this, 5)}>Withdrow</button>
</div>
);
};
export default Counter;
import React from "react";
import { Provider } from "react-redux";
import Store from "../../store/Store";
import CounterReducer from "./CounterReducer";
import createCounterDispatcher from "./createCounterDispatcher";
import Counter from "./components/Counter";
class CounterModule extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.store = new Store(CounterReducer);
this.dispatcher = createCounterDispatcher(this.store);
this.unsubscribeFromStore = () => {
this.store.unsubscribeAll();
};
this.store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState(this.store.getState());
});
}
render() {
return (
<Provider store={this.store}>
<Counter
value={this.store.getState().value}
increment={this.dispatcher.increment}
decrement={this.dispatcher.decrement}
></Counter>
</Provider>
);
}
}
export default CounterModule;
|
自此,我们已经将一个简单的添加和删除通过 Redux 来实现了,我也是按照如下这个状态图来进行一步步改造的,可以将代码和动图结合多看几遍。
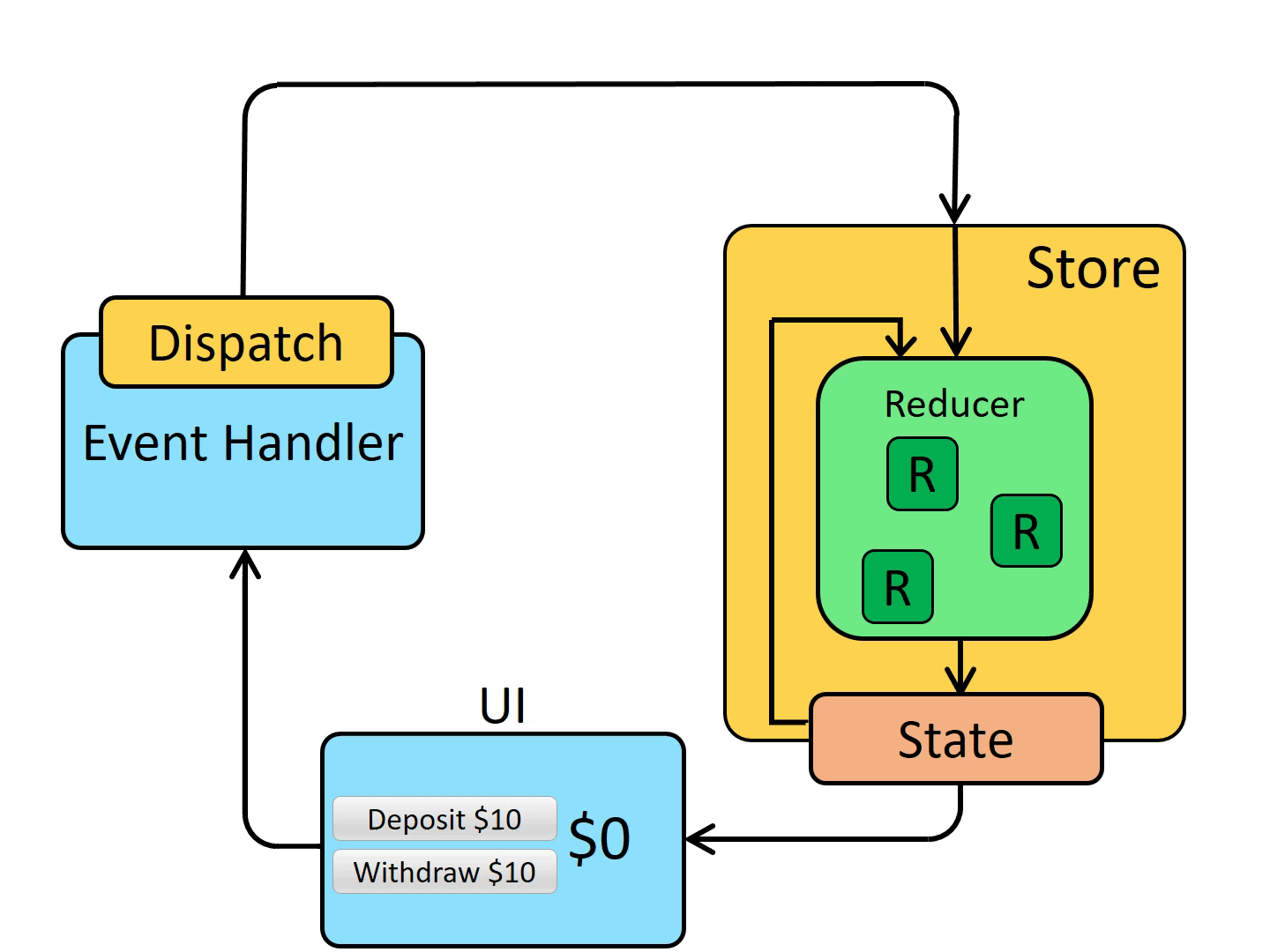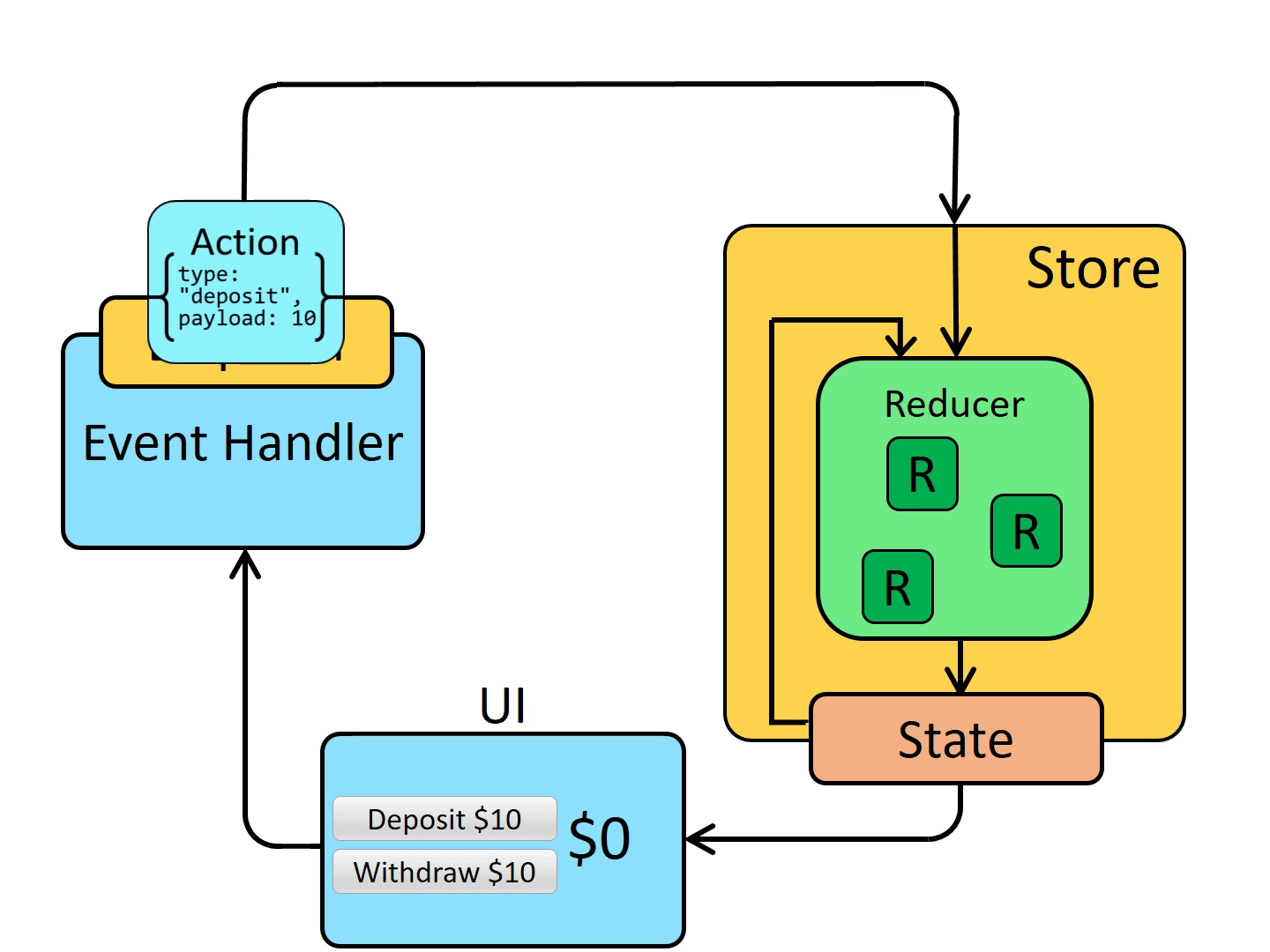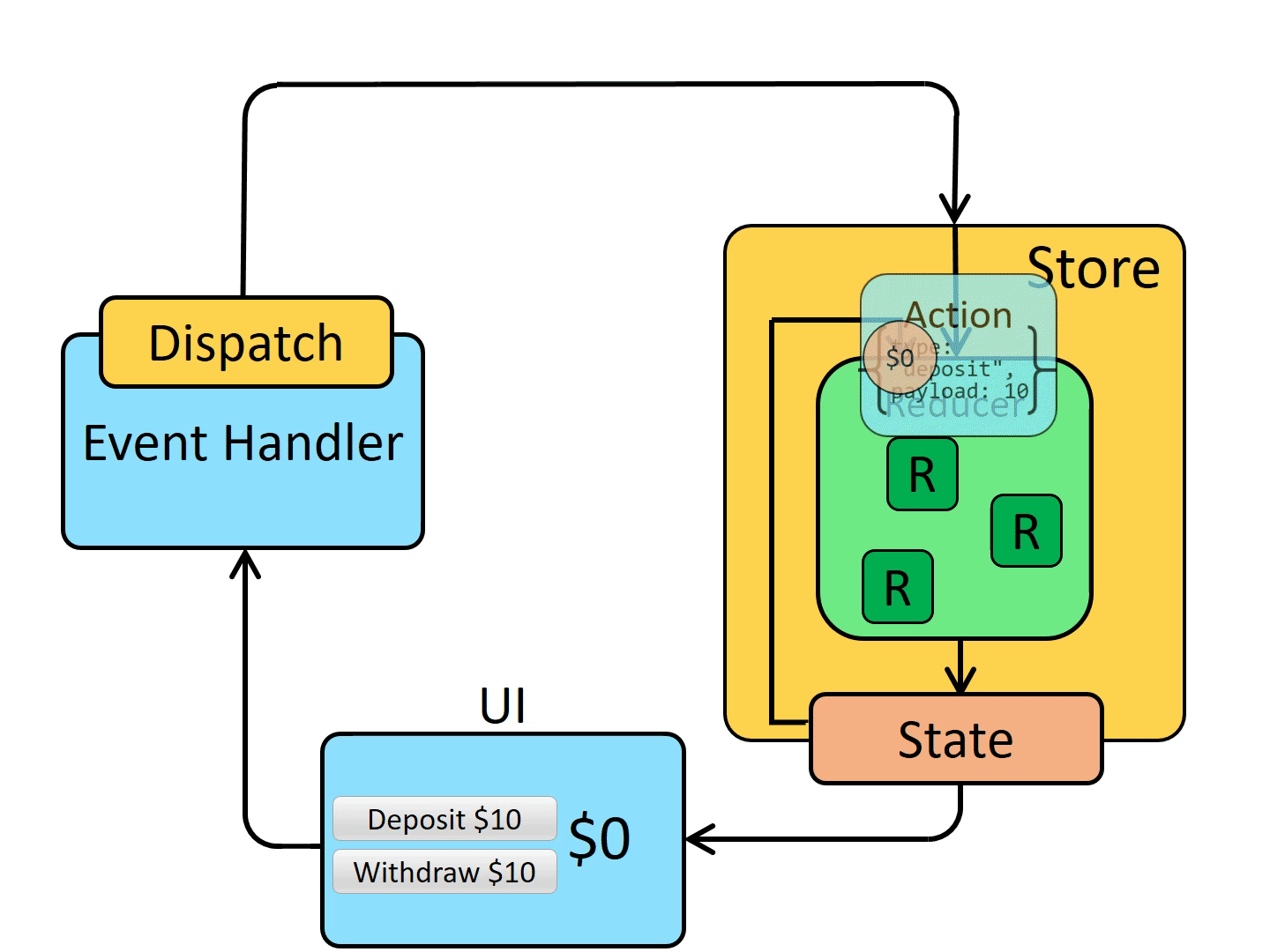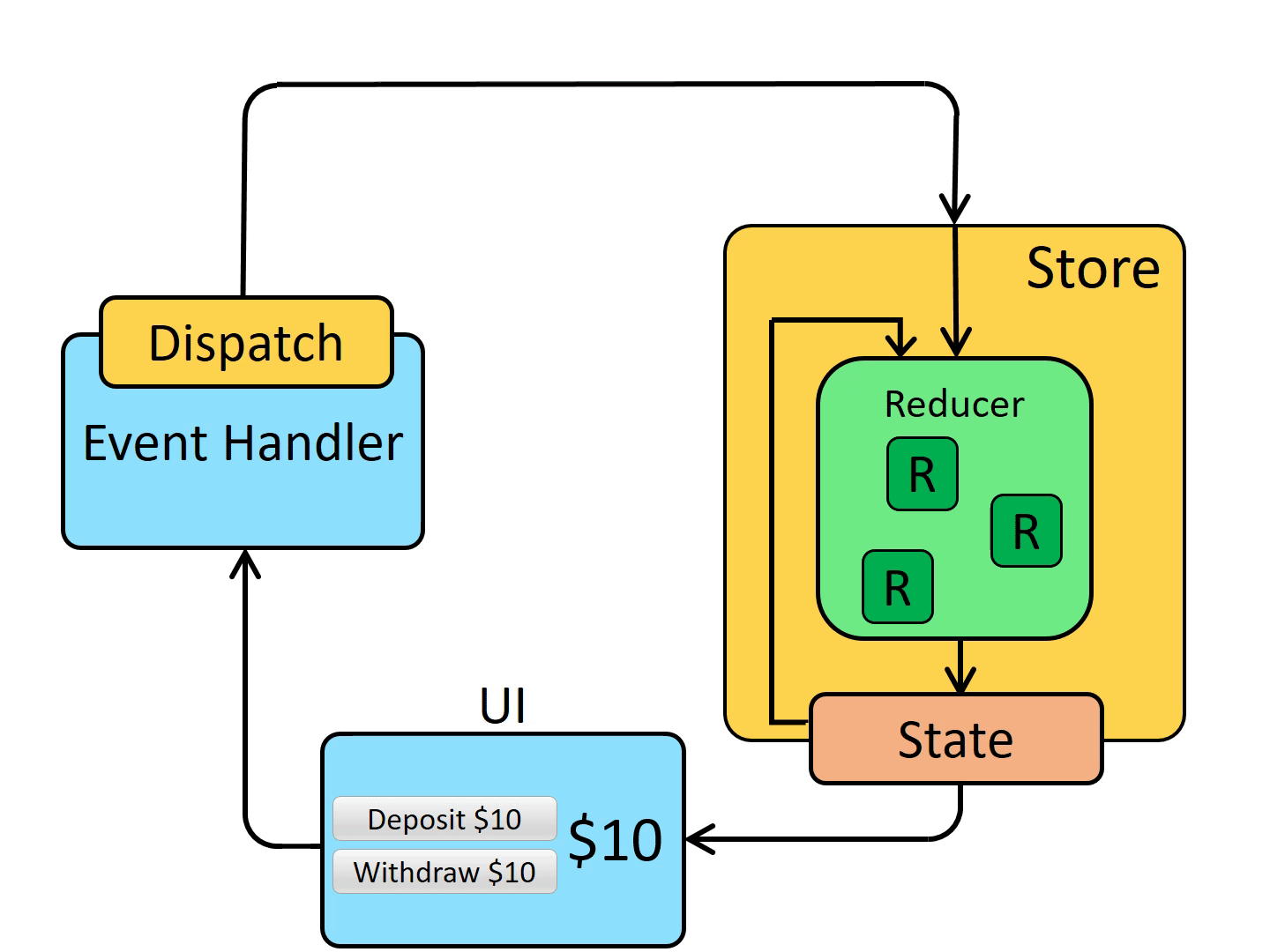
五、优缺点和适用场景
- 优点
- Predictable:可预测的(践行纯函数的思想,不变性)
- Centralized:将应用的状态进行集中化管理(发布-订阅模式)
- Debuggable:配合 Redux DevTools 进行高效调试数据状态
- Flexible:可与任何 UI 层框架搭配使用
- 缺点(可能)
- 有一定的学习曲线,并不适合小型项目
- 存在大量模式代码
- 在观察者模式下,如果观察者和被观察者之间存在依赖,则有可能产生调用死循环
- 所有的状态都在内存维护,如果应用意外崩溃则会导致状态全部丢失了
- 参数传递有些麻烦,需要一层层传(感觉有点违背了 Pub - Sub 的本身思想,但是如果不这样做又会让整个项目太混乱难于维护)
适用场景:由于 Redux 具有严格的状态管理机制,所以当你对组件之间的维护感到吃力时,可以考虑使用 Redux;不要一上来就用,否则是给自己找麻烦。Redux 本身不直接修改状态,只是提供了一种更新状态的方案而已。

